
Editing by David Du
Chinese smartphone maker OPPO has been facing 23 oppositions to the validity of its European patents since June 2020, according to the European Patent Office (EPO) data. The opposing parties mainly include Huawei, Sisvel, 3G Licensing, and a German patent firm.

The EPO data shows that the alleged patents involve standard-essential patents (SEPs) that OPPO bought from Ericsson, Blackberry, Intel, and Panasonic, as well as OPPO-developed patents.
Huawei filed the first opposition in June 2020, attacking one of OPPO’s telecom SEPs it bought from Ericsson. Since then, new oppositions have been filed roughly once a month.
The opposition process under the European Patent Convention (EPC) allows any person to challenge EPO patents. The person must file an opposition within nine months after a patent is granted. An opposition decision can revoke a newly granted patent and is bounding in all EPO member countries, weighing more than a national invalidity decision.
These oppositions appeared to have been planned. For example, 3G Licensing and the German patent firm both filed oppositions to patents on the last day of the nine months after the patents were granted.
3G Licensing and Huawei accounted for most of the oppositions. OPPO has a history in dealing with Sisvel, 3G Licensing’s parent company. In 2013, Sisvel reached out to negotiate licensing deals with OPPO. Failing to reach an agreement, Sisvel sued OPPO in the Netherlands, Italy, and the UK in 2019, accusing the Chinese company of patent infringement.
Sisvel then lost some of the key legal battles against OPPO, which may explain why Sisvel and its subsidiary felt the urge to fight back in the European market. For example, the District Court of The Hague declared Sisvel’s SEP invalid and rejected its injunction request in May 2020. The UK High Court found its 3G patent non-essential and dropped its case in April 2021.
Huawei also has a motive to challenge OPPO’s patents. Huawei’s global shipments reportedly slumped about 40% at the end of 2020 due to U.S. sanctions. As a result, it fell from the world’s No. 1 smartphone maker to a place behind OPPO.
In contrast, OPPO raised as the fourth-biggest smartphone maker in the world in the fourth quarter of 2020, according to Counterpoint Research. Canalys data also shows OPPO’s European market share in the first quarter of 2021 soared 153%, helping it secure fourth place after Samsung, Xiaomi, and Apple.
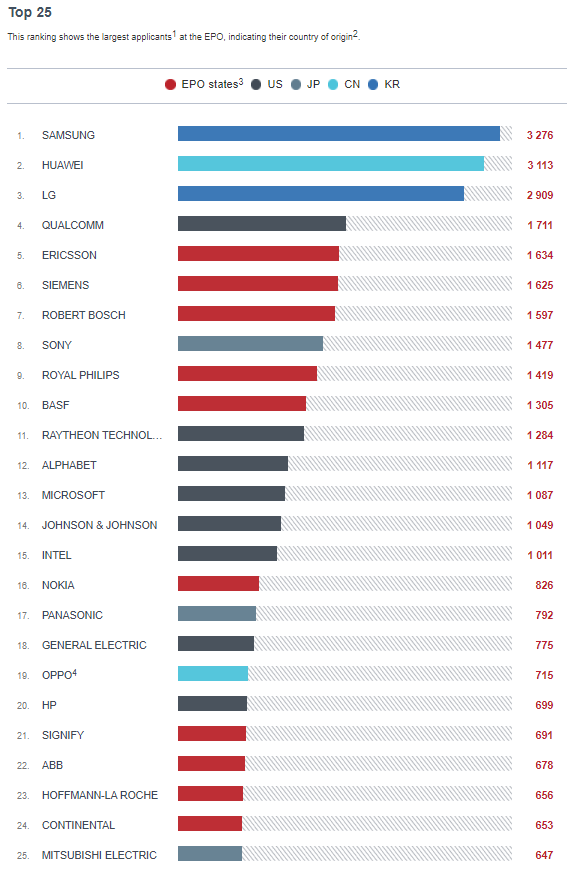
Moreover, Huawei and OPPO were the only Chinese companies among the top 25 EPO patent applicants in 2020, in second and 19th places, respectively, as the EPO Patent Index 2020 shows.
The patent opposed by the German patent firm relates to wearable devices, such as True Wireless Stereo (TWS) earbuds. Although it is unclear as to who instructed the action, the move could be the result of the escalated turf war in the wearable market.
Data from market analysis firm IDC shows that the top 5 wearables brands in the world - Apple, Xiaomi, Huawei, Samsung, and Fitbit - took up nearly 70% of the market share in 2020. It left only a small portion of the market for newcomers to squeeze in.
With a lower market concentration ratio of 84%, compared to China’s 96.5%, Europe is arguably the most sought-after market for Chinese smartphone companies. As OPPO continues to grow its market share and patent strength, there would be more of its rivals to act preemptively.
RELATED
-
Chinese smartphone maker Oppo goes after high-end market in Indonesia after winning largest market share
11-14 15:36 -
WIPO: Chinese companies Huawei, OPPO, and ZTE are the top three in PCT patent applications in 2022
09-22 13:28 -
JW Insights: Huawei's return to 5G smartphones challenges not only Apple but also local leading brands trying to move up to high-end markets
09-12 13:50
READ MOST

No Data Yet~







